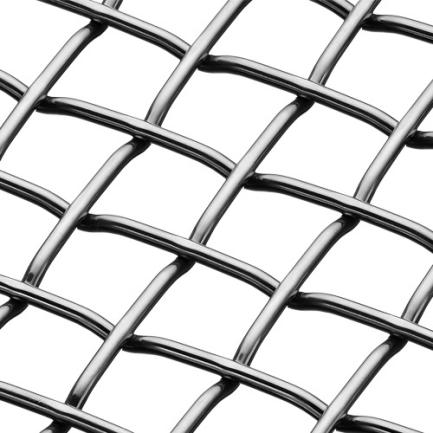
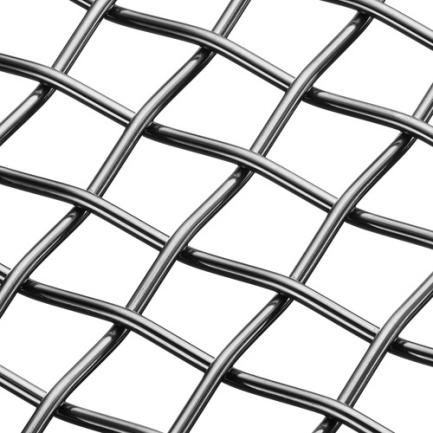
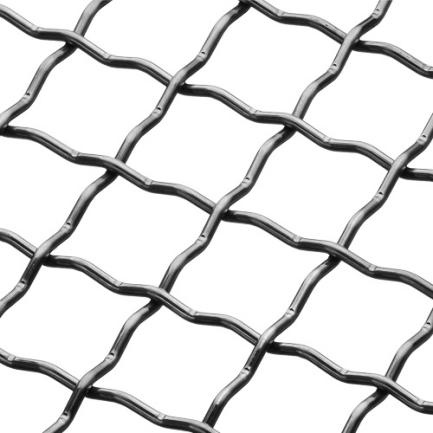
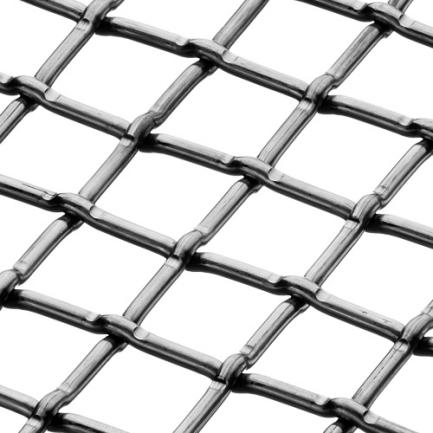
Crimped wire mesh is available in various styles or patterns, each characterized by a unique crimping design. These crimped wire mesh styles offer different appearances, structural properties, and functionality for a wide range of applications. Here are some common crimped wire mesh styles:
Double Crimp:
The double crimp style features crimping in both the warp and weft directions, creating a stable and robust mesh structure.
This style provides excellent rigidity, strength, and stability, making it suitable for applications that require high structural integrity and resistance to deformation.
Lock Crimp:
The lock crimp style incorporates crimped wires with straight sections, which interlock with each other to form a tight and secure mesh pattern.
This style offers enhanced stability, durability, and resistance to shifting or movement, making it suitable for demanding applications that require strong and rigid mesh panels.
Flat Top:
The flat top style has flat, uncrimped wires in the warp direction and crimped wires in the weft direction.
This style provides a smooth and flat surface, making it suitable for applications where a flat mesh surface is required, such as architectural facades or decorative panels.
Intermediate Crimp:
The intermediate crimp style features crimping in both the warp and weft directions, but with smaller crimps compared to double crimp.
This style provides a balance between strength, flexibility, and filtration properties, making it suitable for applications such as screening, sorting, or filtration.
Slotted Crimp:
The slotted crimp style incorporates crimped wires with elongated slots, resulting in a mesh pattern with elongated or diamond-shaped openings.
This style offers improved flow characteristics, reduced clogging, and enhanced screening efficiency, making it suitable for applications such as vibratory screens or dewatering screens.
These are just a few examples of crimped wire mesh styles available in the market. The selection of the appropriate style depends on the specific requirements of the application, including strength, stability, filtration needs, aesthetics, and desired mesh characteristics.